Your Guide to Treating Contact Dermatitis
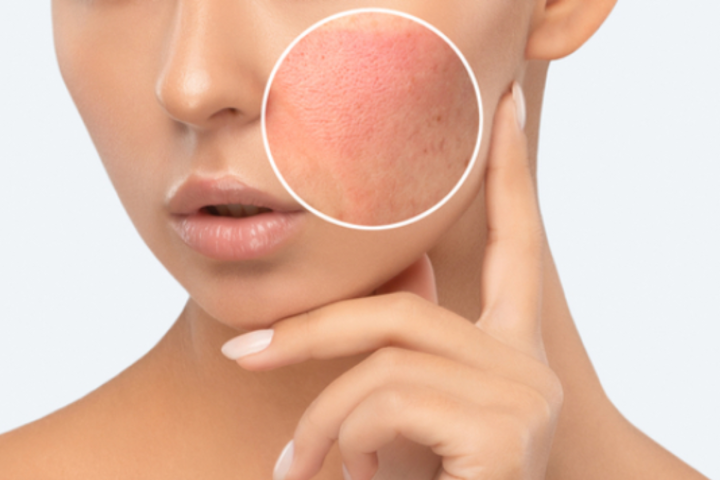
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema (atopic dermatitis) that is caused by contact with a substance that triggers an allergic or irritant reaction. It is a common condition that affects people of all ages, and it can be quite uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatments for contact dermatitis.
What is Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. It is a type of inflammation of the skin caused by contact with irritants or allergens. Symptoms include redness, itching, burning, and swelling of the affected area.
Types of Contact Dermatitis
There are different types of contact dermatitis: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis, and a few more. Let's take a closer look at each of these types and their symptoms.
-
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type of contact dermatitis and occurs when the skin is exposed to an irritant substance. This can include things like soaps, detergents, cleaning products, or even water. Symptoms of irritant contact dermatitis can include redness, itching, burning, and dryness of the affected area. In severe cases, blistering and swelling may occur.
-
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin is exposed to a substance that triggers an allergic reaction, triggered by common allergens like nickel, latex, or certain chemicals. Symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis can include redness, itchy rashes, swelling, and the formation of small blisters or bumps on the affected area. It may take several hours or days after exposure for symptoms to appear.
-
Photocontact dermatitis is a less common type of contact dermatitis that occurs when the skin is exposed to a substance that is activated by sunlight. This can include certain medications, fragrances, or chemicals in cosmetics. Symptoms of photocontact dermatitis can include redness, itching, and blisters. The affected area may also become more sensitive to sunlight.
-
Occupational contact occurs when the skin is exposed to substances in the workplace that cause irritation or an allergic reaction. This can include chemicals, dyes, or even certain types of plants. Symptoms of occupational contact dermatitis can include redness, itching, swelling, and the formation of blisters or bumps.
-
Contact urticaria is a type of contact dermatitis that occurs when the skin is exposed to a substance that causes an immediate allergic reaction. This can include things like insect bites, certain foods, or even latex. Symptoms of contact urticaria can include skin irritation, redness, and the formation of hives or welts on the skin.
Common Causes of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis can be caused by a wide range of substances, including plants, chemicals, metals, and cosmetics. Some of the most common triggers of contact dermatitis include:
-
Poison ivy, poison oak, and sumac
-
Nickel allergy
-
Latex, which is found in gloves and other medical supplies
-
Fragrances and preservatives in skincare products, as well as hair dyes, perfumes, and other cosmetics
-
Cleaning products and other household chemicals
-
Industrial chemicals and solvents
Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis
The symptoms of contact dermatitis can vary depending on the severity of the reaction and the area of the skin that is affected. Common symptoms include:
-
Redness, swelling, crusting, and itching
-
Blisters and oozing
-
Dry, cracked, and scaly skin
-
Burning and stinging sensations
-
Thickened and leathery skin
How to Treat Contact Dermatitis
The treatment for contact dermatitis depends on the severity of the reaction and the cause of the inflammation. Mild cases of contact dermatitis can often be treated with over-the-counter topical creams and ointments, such as hydrocortisone and calamine lotion, which can help reduce itching and inflammation.
For more severe cases, prescription-strength topical steroids such as corticosteroid creams or oral corticosteroids may be necessary to reduce skin reactions. In some cases, antihistamines may also be prescribed to reduce skin problems such as itching and swelling.
Here are some steps you can take to treat contact dermatitis.
Identify the Cause
The first step in treating contact dermatitis is to identify the cause of the irritation. If you can identify the irritant or allergen, then you can avoid it in the future. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, solvents, and chemicals. Allergens can be harder to identify, but common ones include nickel, latex, and fragrances.
Remove the Irritant
Once you have identified the irritant or allergen, you should try to remove it from your skin. If the irritant is still on your skin, it will continue to cause inflammation and irritation. Rinse the affected area with cool water and mild soap, and then pat dry with a clean towel.
Apply a Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help to quell inflammation and itching. You can use a cold, damp cloth or a bag of ice wrapped in a towel. Apply the compress for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Use Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are creams or ointments that can help reduce inflammation and itching. They are available over-the-counter or by prescription, depending on the strength. Follow the instructions carefully, and do not use them for longer than recommended.
Take an Antihistamine
Antihistamines are medications that can help reduce itching and swelling. They are available over-the-counter or by prescription. Follow the instructions carefully, and do not exceed the recommended dose.
Avoid Scratching
Scratching the affected area can make the irritation worse and increase the risk of infection. Try to avoid scratching as much as possible. If you can't resist the urge to scratch, wear gloves or cover the affected area with a bandage.
Moisturize
Keeping the affected area moisturized can help reduce itching and prevent dryness. Use a fragrance-free moisturizer several times a day. Avoid using products that contain alcohol, which can dry out the skin.

We recommend starting with Rainbow’s Hydrate Mask followed by Rainbow’s Hydrate Body Butter to soothe irritated skin. Always follow up with sunscreen!

How to Prevent Contact Dermatitis
The best way to prevent contact dermatitis is to avoid contact with the substances that trigger the reaction. If you know you are allergic to a particular substance, such as poison ivy or nickel, take steps to avoid exposure. This may include wearing protective clothing or gloves, using hypoallergenic personal care products, and avoiding areas where the offending plant or chemical is present.
If you do come into contact with a known allergen or irritant, be sure to wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water as soon as possible. This can help remove the substance from the skin and reduce the severity of the reaction.
If none of the above remedies help, we recommend consulting a dermatologist, allergist, or healthcare provider. You may have other underlying skin conditions or an underlying health problem, like a weakened immune system. A specialist will be able to recommend the best treatment options and home remedies that can help.